Listening to music or talk radio from your car is a great way to pass the time when you’re working in your garage, waiting for your significant other to finish their shopping, or getting away from work on your lunch break.
Obviously, the audio system is powered by your car’s battery, and without the car running it begs the question: How long can I leave the music on in my car and not kill the battery?
A healthy car battery should be able to power the radio at a reasonable volume for 3 to 4 hours and still be able to reliably start the engine.
That’s the quick and easy answer and should give you a ballpark estimate. But if you want to know how long YOUR car battery will power YOUR radio, then you’re in luck.
I went the extra mile though and made a chart that will show you how much time you should expect based on the size of your battery (Cold Cranking Amps, or Amp Hours).
How Long Can a Car Battery Power the Radio
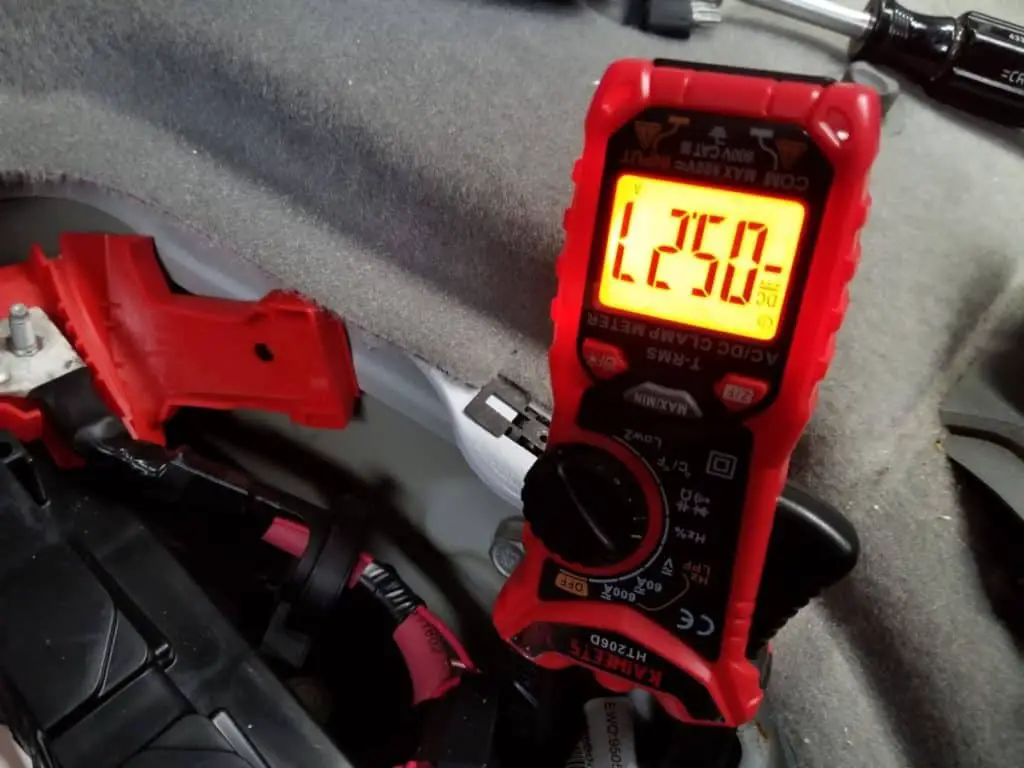
For this table, I went ahead and measured 5 different vehicles of different makes and models to get an average amperage for when the radio is turned on.
I had some below, and some above, but the average was about 4.5 amps with the key turned to ACC and listening to only the radio at a reasonable volume with no other optional electrical items being engaged.
I used a clamp-on multimeter for these measurements.
How Long Can You Listen to the Car Radio (and Still Start the Engine)?
| 75% State of Charge | 50% State of Charge (Half-dead Battery) | 0% State of Charge (Dead Battery) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small Car Battery CCA: 200-315 AH: 36-46.2 | 2.25 Hours | 4.5 Hours | 9 Hours |
| Mid-Sized Car Battery CCA: 315-550 AH: 46.2-58.8 | 2.75 Hours | 5.5 Hours | 11 Hours |
| Large Car Battery CCA: 500-1,000 AH: 58.8-111 | 4.5 Hours | 9 Hours | 18 Hours |
**Assumptions: Battery begins at a full state of charge and is relatively new and healthy. Volume is at a reasonable level with the default speaker system from the manufacturer.
*** Numbers based on an average of 5 vehicles I measured of different makes and models. 4.5 amps was the average draw when listening to the radio at a reasonable level.

How Many Amps Does a Car Radio Use?
On average, a car radio will draw about 4.5 amps from the car battery at a reasonable volume and with the original stereo and audio equipment installed.
When I measured the 5 different vehicles, I found amperage readings from 3.9 to 5.3, but the average was 4.5.
I found that the vehicles with older systems (simple clock radio without touch screens) tended to be on the bottom end, while those with touch screens were the highest.

It’s understandable that the newer systems would be a little more power-hungry, as the actual head units are equipped with more features that are automatically engaged or placed on standby when you are only intending on listening to the radio. GPS, voice commands, the display lighting itself, Bluetooth capabilities, etc. are just some of the extra features.
Audio and stereo equipment that was installed during the manufacturing process is probably going to be lower in both power consumption and performance. There’s an entire market dedicated to souping up the audio features in vehicles (better speakers and bass, especially), and doing so is almost always going to add more draw to your vehicle’s battery.
I also noticed that there was no reliable and noticeable difference in the amp reading when playing a CD or when connecting my phone to the speakers via an auxiliary jack. Perhaps my multimeter is not sensitive enough to pick up.
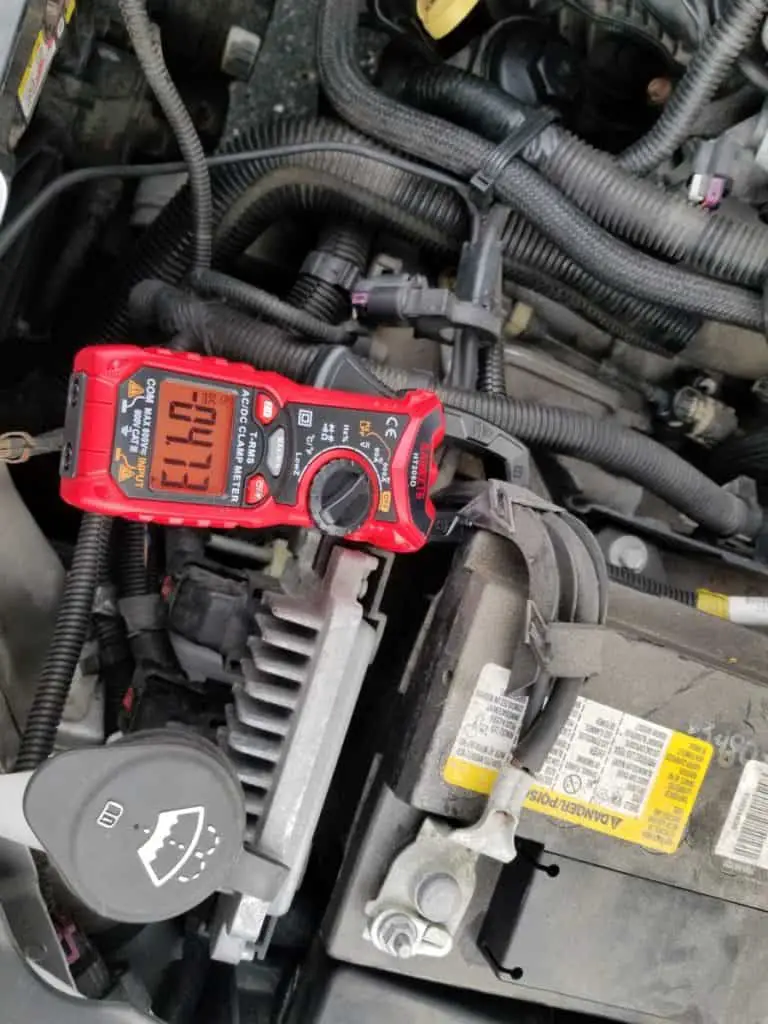

How Many Amps Does My Car Battery Have?
I wrote an article that you can check out here that covers how many amp-hours you can expect out of a particular car battery based on its sticker, so I won’t get into too many details here and I’ll keep it short.
A car battery is typically rated in CCA (cold cranking amps) due to the fact that it’s a starting battery and it was not engineered for use with a long-term draw on it like a deep-cycle marine or golf cart battery.
Using your car battery to power anything long-term without running the engine so that the alternator simultaneously charge your car’s battery will lead to a very short lifespan.
A small car battery with a 200-315 CCA rating will be about 36-46.2 amp-hours. A mid-sized battery with 315-550 CCA will be 46.2-58.5 amp-hours. A large car battery with 550-1,000 CCA will have a 58.5-111 amp-hour equivalency.
Amp Hour Estimates Based On Cold Cranking Amps or Reserve Capacity
| If Your Sticker Reads: 200-315 CCA, or 40-60 RC | If Your Sticker Reads: 315-550 CCA, or 60-80 RC | If Your Sticker Reads: 550-1,000 CCA, or 80-190 RC |
| 36 - 46.2 AH | 46.2 - 58.8 AH | 58.8 - 111 |
Will My Car Battery Get Ruined by Listening to the Radio (with the Engine Off)
Dabbling with listening to music while the engine is off isn’t ideal for long periods of time, but a half-hour to an hour isn’t going to make a noticeable difference in battery performance unless your battery is already on the edge.
If you do decide to listen to the radio for a considerable amount of time, it is best to run your engine afterward and preferably drive your vehicle to let the alternator charge the battery again. Failure to do so will allow sulfation to build up and your battery’s lifespan will reduce significantly.
Car batteries are starter batteries and were engineered to be able to release a short burst of very high amperage in order to turn over the engine. They were not designed for, and are easily damaged by prolonged deep-discharges through sulfation.
Sulfation occurs naturally when your battery is not at a full state of charge, and the more your battery is depleted, the faster it will sulfate.
Sulfation is when the lead plates inside the battery get coated with a white crystalline substance called lead sulfate. This coating not only reduces the ability of your battery to release energy to start your engine but also reduces its ability to receive a full charge. In time, it leads to a vicious circle where the battery gets worse and worse.
After 10-12 complete deep discharges, a car battery will not be able to recharge again due to sulfation. You’ve only got several dozen partial deep discharges to work with so use them wisely!
Listen to Your Favorite Music without Damaging the Car Battery
If you’re just planning on using your car’s stereo system every once in a while while you wait in a parking lot, then party on. You shouldn’t notice any measurable difference in your battery’s lifespan.
If, however, you find yourself wanting to listen to music on the beach, in your garage, in the driveway, or while camping, then you are better served to have a dedicated means of making those beautiful sound waves than damaging your car’s battery in the process.
Having a compact, portable, rechargeable, and Bluetooth-enabled speaker is the best option for meeting your audio needs and ensuring that you’ll be able to start your engine.
If you’re looking for amazing sound quality that you can pair with your phone and with 12 hours of runtime, then you can’t beat this deal on Amazon.
If you’re looking for a rugged option that won’t break the bank while still having good sound quality, then I would recommend looking into this option.